What Is an FPGA? Everything You Need to Know About the Magic of Programmable Chips
2025-03-26 11:27:47 1382
The Field Programmable Gate Array, or FPGA, is a device that is frequently referred to as the "LEGO of hardware" in the field of electronics. It may be operating covertly inside gadgets all around you, including 5G base stations, driverless cars, and even spacecraft, even if you are unaware of its name. This article will explain what an FPGA is, how it functions, its applications, and how it stacks up against more conventional devices like MCUs and ASICs.
1. What Is an FPGA? Explained in One Simple Sentence
An FPGA is a chip that may be reprogrammed to carry out various hardware functions once it has been manufactured. Its primary advantage is that it is "reconfigurable," which allows you to create your own logic circuits, much like developing software for hardware. For highly tailored, low-latency, and high-performance applications, this makes it perfect.
2. Key Features of FPGA: Flexible, Parallel, Customizable, Real-Time
Programmability of Hardware
FPGAs, in contrast to fixed-function chips, can be set up to do any logic your project requires, even after the device is in your possession.
Processing in True Parallel
FPGAs can do multiple tasks at once, in contrast to CPUs that only handle one activity at a time. For the appropriate tasks, this leads to significant performance increases.
High Real-Time Responsiveness and Low Latency
FPGAs reduce response delay, making them ideal for time-sensitive applications like high-speed image recognition or industrial automation.
Extended Life Cycle of a Product
As market demands change, you may reprogram the FPGA logic, enabling your hardware to adjust without having to completely reinvent the system.
3. How Does an FPGA Work? From Programming to Blinking an LED
Thousands of logic elements—think of them as digital building blocks—are found inside an FPGA. There are millions of possible connections between these.
With a Hardware Description Language (HDL) such as Verilog or VHDL, you can program it by defining logic such as "if input is HIGH, turn the LED ON." After compilation, this code is transformed into a configuration that instructs the FPGA on how to connect its internal logic.
Consequently, a blank chip turns into a completely unique hardware system that you have built.
4. What is FPGA used for: From Earth to Orbit
Telecommunications
FPGAs process enormous volumes of real-time data in optical networks and 5G base stations.
Deep Learning and AI
FPGAs are excellent for matrix operations and are being utilized more and more to speed up neural networks and machine learning algorithms.
Robotics and Industrial Automation
For precise operations like machine vision and robotic arms, FPGAs offer ultra-low latency deterministic control.
Automobile Systems
FPGAs enable real-time sensor fusion and decision-making for ADAS (Advanced Driver Assistance Systems) and autonomous driving.
Defense & Aerospace
FPGAs are frequently selected for satellites, radar systems, and other mission-critical platforms because of their dependability and radiation resistance.
5. FPGA vs MCU vs ASIC: How to Choose?
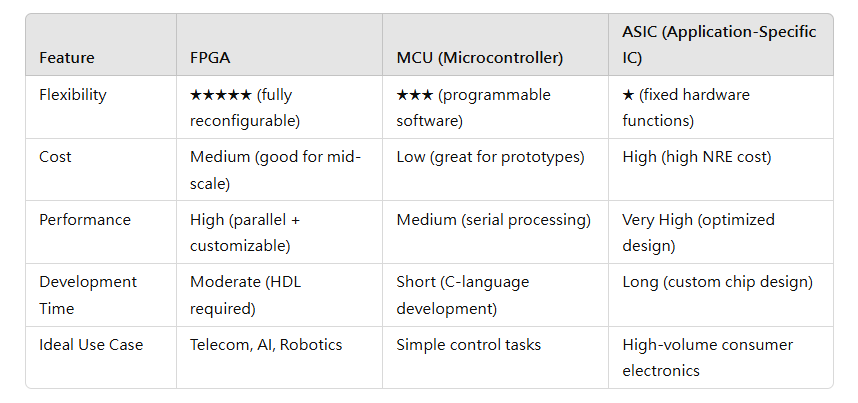
Figure. 1
6. Is FPGA the Future? Or Already the Present?
High-performance, adaptable hardware is becoming more and more necessary as edge computing, AIoT, and smart mobility develop. FPGA, which falls between stiff ASICs and general-purpose MCUs, is becoming more and more popular. Due to significant investments from industry titans like Intel, AMD, and Xilinx, FPGAs are now not only more potent but also more widely available than before.
In Conclusion: FPGA Isn’t the Future—It’s Already Everywhere
Even while FPGA can appear to be a specialized tool for engineers, it is already influencing technology in our daily lives. Behind the scenes, FPGA functions as a programmable "super team," quickly transforming concepts into hardware for everything from controlling autonomous devices to broadcasting HD video.
Are you interested in finding out more about FPGA development, applications, and recommended chips? For future in-depth courses, guides, and industry insights geared toward both novices and experts, follow us.




