TPS2530DBVR Power Distribution Switches: Features, Applications and Datasheet
2025-09-02 14:47:40 630
TPS2530DBVR Description
The TPS2530DBVR is a precision current-limited power distribution switch optimized for USB and general power management applications. It integrates a low on-resistance MOSFET with accurate current limiting and overcurrent protection, ensuring reliable operation of downstream devices. This device is particularly useful for protecting host systems against short circuits, overloads, or device faults while complying with USB power delivery requirements. Packaged in a compact SOT-23-6 (DBV) form factor, it provides a cost-effective solution for power control in portable and embedded systems.
TPS2530DBVR Features
Input voltage range: 2.7 V to 5.5 V, optimized for USB VBUS operation.
Integrated 70 mΩ (typ.) MOSFET, minimizing conduction losses.
Precision current-limit settings with ±6% accuracy for reliable load protection.
Overcurrent, short-circuit, and thermal shutdown protection for robust system safety.
Reverse current blocking to prevent damage from reverse voltage conditions.
Fault reporting via active-low open-drain FLAG pin.
Small footprint: 6-pin SOT-23 package, suited for compact boards.
TPS2530DBVR Applications
USB host and hub power switching (notebook PCs, tablets, docking stations).
Set-top boxes and smart TVs for USB device power management.
Portable electronics (handheld devices, MP3 players, portable storage).
Embedded systems requiring current-limited 5 V rails.
General-purpose power distribution in industrial or consumer electronics.
TPS2530DBVR CAD Model
Symbol

Footprint
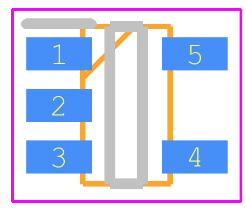
3D Model
TPS2530DBVR Alternatives
TPS2553 – Adjustable current-limit power switch with similar protection features.
TPS2065C – High-side USB power switch with slightly different current ratings.
MIC2005A (Microchip) – Low-voltage power distribution switch alternative.
AP2553 (Diodes Inc.) – USB-compliant current-limited power switch.
TPS2530DBVR Manufacturer
Texas Instruments Incorporated (TI) is a global leader in the design and manufacturing of semiconductors and integrated circuits. Headquartered in Dallas, Texas, USA, the company was founded in 1930 and has since become one of the most influential names in the electronics industry. TI develops thousands of products that power everything from industrial automation, automotive systems, consumer electronics, communication equipment, to personal devices.
TI is best known for its analog chips and embedded processors, which are the building blocks of modern electronic systems. Analog products from TI handle real-world signals—such as sound, temperature, or power—while embedded processors provide the digital intelligence required to control devices efficiently. This unique mix enables TI to play a critical role in advancing energy efficiency, connectivity, and system performance across industries.
With a strong focus on innovation, high-volume manufacturing, and long product lifecycles, Texas Instruments supports engineers, manufacturers, and developers worldwide in turning ideas into reality. Today, TI continues to push the boundaries of technology by making electronics smaller, smarter, and more reliable, impacting millions of lives every day.
TPS2530DBVR FAQs
What is the maximum continuous output current the TPS2530DBVR can support?
It can deliver up to 2.0 A continuous output current, depending on ambient temperature and board layout.
How does the TPS2530DBVR indicate a fault condition?
Faults such as overcurrent or thermal shutdown are reported via the active-low FLAG pin, which can be connected to a microcontroller for system monitoring.
What protection mechanisms are integrated into the device?
It includes current limiting, thermal shutdown, and reverse current blocking to protect both the host and connected devices.
Can the current limit be adjusted externally?
Yes, the ILIM pin allows external resistor programming of the current limit, enabling precise compliance with USB load requirements.
What is the typical turn-on time of the TPS2530DBVR?
The device features a controlled rise time of ~1 ms, which helps reduce inrush current during hot-plug events.




