EP4CE55U19I7N FPGAs: Features, Applications and Datasheet
2025-08-04 14:49:54 1026
EP4CE55U19I7N Description
The EP4CE55U19I7N is a high-performance, low-power FPGA from Intel’s Cyclone IV E family, designed for cost-sensitive applications requiring medium-to-high logic density. Built on a 60 nm low-power process, it delivers an excellent balance of performance, power efficiency, and cost, while supporting rich I/O standards and embedded memory blocks. Its compact UFBGA-484 package makes it suitable for space-constrained designs while maintaining high pin counts for connectivity.
EP4CE55U19I7N Features
Logic Elements (LEs): ~55,000
Embedded Memory: ~2.5 Mbits distributed in M9K memory blocks
Package: UFBGA-484, ideal for high-density and space-limited boards
Operating Temperature Range: Industrial grade (–40°C to +100°C)
Clock Management: Multiple PLLs for clock synthesis and phase alignment
Low Power Design: Optimized for energy-efficient systems
I/O Standards Support: LVTTL, LVCMOS, LVDS, SSTL, and HSTL
Configuration Modes: JTAG, Active Serial (AS), Passive Serial (PS), and Fast Passive Parallel (FPP)
DSP Blocks: Includes dedicated multipliers for high-speed arithmetic processing
EP4CE55U19I7N Applications
Industrial Control Systems: Motion control, robotics, and automation
Communication Systems: Baseband processing, packet switching, and protocol bridging
Consumer Electronics: High-definition video processing and display controllers
Embedded Systems: Microcontroller augmentation and real-time data acquisition
Networking Equipment: Routers, switches, and access points requiring LVDS interfaces
Medical Electronics: Imaging and real-time monitoring systems
EP4CE55U19I7N CAD Model
Symbol
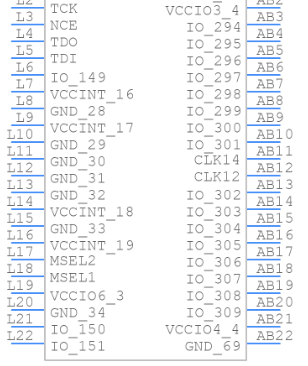
Footprint
3D Model

EP4CE55U19I7N Alternatives
Intel Cyclone V 5CEFA5F23I7N (higher performance and system integration)
Lattice ECP5 LFE5U-45F (compact, low-power with strong DSP support)
Xilinx Artix-7 XC7A50T-2FGG484I (similar logic density, better DSP throughput)
Microchip PolarFire MPF050T-1FCVG484I (for ultra-low power and security-critical designs)
EP4CE55U19I7N Manufacturer
Intel Corporation is a global technology leader headquartered in Santa Clara, California, best known as one of the world’s largest and most influential semiconductor manufacturers. Founded in 1968 by Robert Noyce and Gordon Moore, Intel pioneered the development of the microprocessor, powering the personal computing revolution and setting standards in digital innovation.
Today, Intel’s portfolio extends beyond CPUs to include FPGAs, GPUs, AI accelerators, networking solutions, and advanced foundry services, enabling breakthroughs in cloud computing, data centers, artificial intelligence, autonomous driving, and 5G networks. With a strong commitment to research, manufacturing excellence, and sustainability, Intel continues to shape the future of technology, driving a smarter and more connected world.
EP4CE55U19I7N FAQs
What is the maximum number of LVDS pairs supported by EP4CE55U19I7N?
The EP4CE55U19I7N supports up to 66 differential LVDS pairs, making it suitable for high-speed serial data transmission in communications and display systems.
How does the industrial temperature rating affect deployment in real-world systems?
The –40°C to +100°C rating ensures reliable operation in harsh environments such as outdoor telecom base stations and industrial automation systems exposed to variable conditions.
Does the EP4CE55U19I7N support partial reconfiguration?
No, Cyclone IV devices do not support partial reconfiguration; full reconfiguration is required when updating logic designs. For partial reconfiguration, higher-end families like Stratix or Arria are recommended.
What is the maximum operating frequency of internal logic for this FPGA?
Typical internal logic can operate at ~250 MHz, with PLL-assisted clock domains supporting even higher rates depending on design optimization.
How does the power consumption of EP4CE55U19I7N compare with similar density FPGAs?
Thanks to Intel’s 60 nm low-power process, the EP4CE55U19I7N consumes 15–20% less static power than many competing devices in the same density class, making it suitable for battery-powered or thermally constrained systems.




