EN63A0QI DC-DC Converters: Features, Applications and Datasheet
2025-11-05 10:27:59 1244
EN63A0QI Description
The EN63A0QI is a high-efficiency, fully integrated DC-DC step-down power module from Intel (formerly Enpirion). It combines a switching regulator, inductor, MOSFETs, and compensation circuitry in a compact package to provide a complete power solution for point-of-load (POL) applications. The device delivers up to 6 A continuous output current, offering a small footprint and low noise operation ideal for space-constrained designs.
EN63A0QI Features
Input Voltage Range: 2.375 V to 6.0 V
Output Voltage Range: 0.6 V to VIN
Output Current: Up to 6 A continuous
High Efficiency: Up to 95% at full load
Integrated Inductor & MOSFETs: Simplifies PCB design and reduces EMI
Fast Transient Response: Optimized control architecture for dynamic load changes
Soft-Start & Power Good Signal: Ensures safe power sequencing
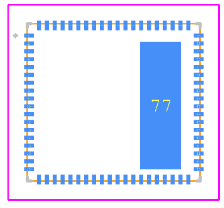
Compact Package: 7 mm × 7 mm × 1.85 mm QFN module
Thermal Shutdown and Overcurrent Protection: Improves system reliability
EN63A0QI Applications
FPGA, ASIC, and DSP core power supplies
High-density telecom and networking systems
Industrial control systems and embedded computing
Server, storage, and data center applications
Portable instrumentation and test equipment
EN63A0QI CAD Model
Symbol

Footprint
3D Model

EN63A0QI Alternatives
If EN63A0QI is not available, consider:
EN6337QI – 6 A high-efficiency POL converter (similar performance, slightly different control characteristics)
EN6347QI – 4 A fully integrated DC-DC converter module
TI LMZ23606 – 6 A SIMPLE SWITCHER® power module from Texas Instruments
Murata OKI-78SR-6/1.5-W36-C – Compact switching regulator alternative
Analog Devices LTM4626 – µModule® DC/DC converter with 6 A output
EN63A0QI Manufacturer
Intel Corporation is a global leader in semiconductor design and manufacturing, headquartered in Santa Clara, California, USA. Founded in 1968 by Robert Noyce and Gordon Moore, Intel is best known as the pioneer of the microprocessor, the fundamental component that powers computers, servers, and countless electronic devices today.
As one of the world’s largest semiconductor companies, Intel develops advanced computing and connectivity technologies across a wide range of markets — from personal computers (PCs) and data centers to artificial intelligence (AI), cloud computing, network infrastructure, and autonomous systems.
Intel’s portfolio includes CPUs, FPGAs, SoCs, chipsets, network controllers, and power management ICs, as well as innovative packaging and process technologies. With its transition toward Intel Foundry and investments in cutting-edge EUV manufacturing and 3D transistor architectures (Intel 4, Intel 3, Intel 20A), the company continues to drive Moore’s Law forward.
Through a commitment to innovation, sustainability, and digital transformation, Intel enables the world’s most influential technologies — powering everything from cloud servers and AI accelerators to 5G networks and smart edge devices.
EN63A0QI FAQs
What switching frequency does the EN63A0QI operate at?
The device typically operates at a 3 MHz fixed switching frequency, allowing for a compact inductor and low output ripple.
Can the EN63A0QI support dynamic voltage scaling (DVS)?
Yes. The output voltage can be dynamically adjusted via the feedback (FB) pin or digital control, enabling power optimization for FPGAs or processors.
What is the typical efficiency at 5 V input and 3.3 V output?
Efficiency reaches approximately 93% at 3 A load, and around 90–91% at full 6 A load.
Does the module require external compensation or loop tuning?
No. The EN63A0QI includes internal compensation optimized for a wide range of output capacitors, simplifying design.
How should the EN63A0QI be laid out on a PCB for optimal thermal performance?
Place multiple thermal vias under the exposed pad to the ground plane and ensure sufficient copper area for heat dissipation.




