EN6337QI DC-DC-Converters: Features, Applications and Datasheet
2025-10-31 14:48:08 763
EN6337QI Description
The EN6337QI is a synchronous buck DC-DC converter power module that delivers up to 6A continuous output current. It integrates the controller, MOSFETs, inductor, and passive components into a single compact package, minimizing external design complexity. Designed for high-efficiency point-of-load (POL) power conversion, it provides a fast transient response and tight voltage regulation, ideal for powering FPGAs, ASICs, and processors.
EN6337QI Features
Wide Input Voltage Range: 2.4V to 6.6V
Output Voltage Range: 0.6V to 5.5V (programmable)
Output Current: Up to 6A continuous
High Efficiency: Up to 95% typical efficiency
Integrated Components: Includes controller, power FETs, inductor, and compensation network
Fast Transient Response: Optimized control architecture for dynamic load changes
Protections: UVLO, OCP, OTP, and short-circuit protection
Soft-Start & Power-Good Signal: Ensures smooth startup and system reliability
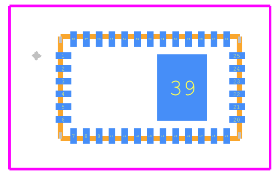
Compact Package: 10mm × 10mm × 4.3mm QFN for space-constrained designs
EN6337QI Applications
FPGA, DSP, and ASIC core power supplies
Network and telecom equipment
Industrial and embedded control systems
High-performance computing and storage
Consumer electronics requiring compact, efficient power
EN6337QI CAD Model
Symbol
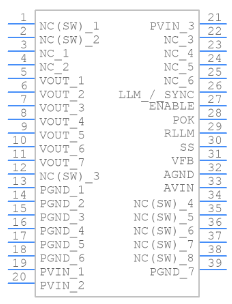
Footprint
3D Model

EN6337QI Alternatives
EN6347QI – 10A version for higher current applications
EN6338QI – 8A module offering similar performance with more power headroom
TPSM84624 (Texas Instruments) – 6A step-down module with wide VIN range
LTM4622 (Analog Devices) – Dual 2.5A/5A μModule regulator for compact designs
EN6337QI Manufacturer
Intel Corporation is a global leader in semiconductor innovation and computing technology, headquartered in Santa Clara, California, USA. Founded in 1968, Intel is renowned for developing advanced microprocessors, chipsets, and integrated circuit solutions that power a wide range of devices — from personal computers and servers to cloud infrastructure and embedded systems.
Driven by continuous innovation, Intel’s portfolio extends across artificial intelligence (AI), 5G connectivity, autonomous driving, and edge computing. Through its cutting-edge process technologies and architectures, Intel enables intelligent computing everywhere, delivering performance, energy efficiency, and scalability for modern digital transformation.
Today, Intel continues to shape the future of technology by advancing Moore’s Law and fostering an open ecosystem that empowers industries worldwide.
EN6337QI FAQs
What control topology does the EN6337QI use?
The EN6337QI employs a current-mode control architecture with integrated compensation, which provides fast transient response and stable operation across wide load and input conditions.
What is the switching frequency of the EN6337QI?
It operates at a nominal switching frequency of 4 MHz, allowing for a compact inductor design and reduced output ripple without compromising efficiency.
How is thermal management handled in the EN6337QI?
The device features an exposed thermal pad for heat dissipation, and the internal power stage is optimized for high efficiency to minimize thermal losses, allowing operation in dense system layouts.
Can the EN6337QI be used in parallel configurations for higher current?
No, the EN6337QI is not designed for current sharing or parallel operation. For higher output current, Intel recommends using higher-rated modules such as the EN6347QI or EN6360QI.
How does the EN6337QI support sequencing in multi-rail systems?
The module features a Power-Good (PG) signal and enable pin, allowing precise control and sequencing with other power rails — essential in systems with multiple voltage domains like FPGAs.




