PCA9555PW I/O Expanders:Features, Applications and Datasheet
2025-08-20 10:37:47 1026
PCA9555PWR Description
The PCA9555PWR is a 16-bit I²C- and SMBus-compatible I/O expander from NXP Semiconductors, offered in a TSSOP-24 package. It provides two 8-bit parallel input/output ports that can be independently configured as inputs or outputs. By adding this device, a system designer can expand GPIO resources without modifying the microcontroller or processor. It supports interrupt output for input change detection, making it highly suitable for event-driven applications in embedded and industrial systems.
PCA9555PWR Features
16-bit configurable I/O: Two 8-bit ports (Port 0 and Port 1), each pin programmable as input or output.
I²C/SMBus interface: Standard two-wire serial control with up to 400 kHz clock rate.
Hardware addressability: 3 address pins allow up to 8 PCA9555 devices on the same bus, enabling 128 I/O lines expansion.
Interrupt capability: Active-low INT output pin for monitoring input changes without constant polling.
Low power: Typical supply current of only a few µA in standby mode, minimizing system power draw.
Wide voltage range: Operates from 2.3 V to 5.5 V, compatible with both 3.3V and 5V systems.
Latch-up protection: Internal ESD protection and fail-safe I²C inputs enhance system robustness.
PCA9555PWR Applications
Consumer electronics: Expanding GPIO for keypads, touch sensors, or LEDs in smart home devices and TVs.
Automotive systems: Control of dashboard indicators, switches, and input scanning in infotainment.
Industrial automation: Multiplexed sensor inputs, signal monitoring, or relay/actuator control.
Embedded systems: Adding pushbuttons, status LEDs, or signal monitoring to microcontrollers with limited I/O.
Networking equipment: System status monitoring and front-panel LED control in routers or switches.
PCA9555PWR CAD Model
Symbol
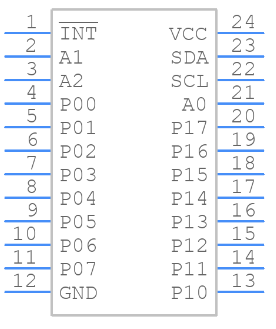
Footprint
3D Model

PCA9555PWR Alternatives
If you need similar GPIO expanders, consider:
PCA9535 – Functionally similar, but with slightly different pin configuration.
PCF8575 – Another NXP I²C expander, 16-bit, more cost-effective for basic applications.
TCA9555 (Texas Instruments) – Drop-in functional equivalent with similar register set.
MCP23017 (Microchip) – 16-bit I²C I/O expander, but with a different internal register map and slightly different interrupt handling.
PCA9698 – High-density 40-bit I²C I/O expander for larger systems needing more GPIO in one IC.
PCA9555PWR Manufacturer
Texas Instruments Incorporated (TI) is a global semiconductor company headquartered in Dallas, Texas, USA, founded in 1930 (originally as Geophysical Service Incorporated). TI is one of the world’s largest and most established chipmakers, well known for its analog and embedded processing products.
TI’s portfolio includes power management ICs, signal chain devices, microcontrollers (MCUs), processors, and DLP® technology, serving industries ranging from automotive, industrial, communications, and personal electronics, to education. With a strong focus on analog semiconductors, TI enables energy efficiency, high-performance signal processing, and smarter electronics design.
The company also has a significant presence in education technology, especially with its TI-84 and TI-Nspire graphing calculators, widely used in schools and universities worldwide.
Today, TI operates with a mission to create a better world through semiconductor innovation, continuously investing in manufacturing capacity, long-term supply assurance, and R&D, positioning itself as a trusted partner for engineers and system designers.
PCA9555PWR FAQs
How many PCA9555PWR devices can share a single I²C bus?
Up to 8 devices, determined by the 3 hardware address pins, allowing a total of 128 I/Os.
What happens to the I/O pins after power-up or reset?
All I/O pins default to input mode to prevent accidental drive conflicts with other devices.
Does the PCA9555PWR support both level detection and edge detection for interrupts?
The device generates an active-low interrupt on any input state change; the host must read the input port to determine the cause (edge detection must be implemented in firmware).
What is the maximum sink/source capability of each I/O pin?
Each output pin can typically sink about 10 mA (suitable for LEDs) but should not be used for high-current loads without external drivers.
Can the PCA9555PWR tolerate a higher voltage on I/O pins than VCC?
No, the I/O pins are referenced to VCC. They should not exceed VCC + 0.5 V; for mixed-voltage designs, level-shifting or voltage translation is required.




