EPM1270T144C5N CPLDs: Features, Applications and Datasheet
2024-10-22 09:49:02 584
EPM1270T144C5N Description
EPM1270T144C5N is a programmable logic device (PLD) from the Altera MAX II family. It features high-performance, low-power consumption, and in-system programmability (ISP). This device is suitable for a wide range of applications, including communications, industrial control, and consumer electronics.
EPM1270T144C5N Features
High-performance CPLD architecture
In-system programmability (ISP) via JTAG interface
Low power consumption
High-speed CMOS technology
Up to 1270 macrocells
144-pin plastic TQFP package
EPM1270T144C5N Applications
Communications equipment
Industrial control systems
Consumer electronics
Data processing systems
Test and measurement equipment
EPM1270T144C5N CAD Model
Symbol
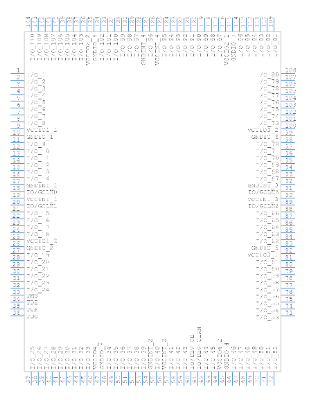
Footprint
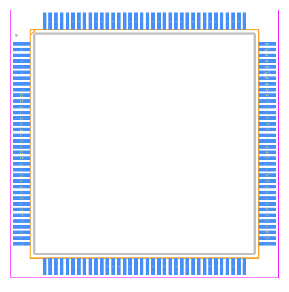
3D Model
EPM1270T144C5N Alternatives
Some alternatives to EPM1270T144C5N include other PLDs from different manufacturers or within the Altera product line, such as:
Xilinx CPLDs
Lattice CPLDs
Other Altera MAX II devices with similar specifications
EPM1270T144C5N FAQs
Questions: What is the programming interface for EPM1270T144C5N?
Answer: The programming interface for EPM1270T144C5N is JTAG (Joint Test Action Group).
Questions:What is the power consumption of EPM1270T144C5N?
Answer: EPM1270T144C5N features low power consumption, but the exact value depends on the operating conditions and configuration.
Questions:Is EPM1270T144C5N available in different package sizes?
Answer: Yes, EPM1270T144C5N is available in a 144-pin plastic TQFP package.
Questions:Can EPM1270T144C5N be programmed in-system?
Answer: Yes, EPM1270T144C5N supports in-system programmability (ISP) via the JTAG interface.
Questions:What are the main differences between EPM1270T144C5N and other PLDs in the Altera MAX II family?
Answer: The main differences between EPM1270T144C5N and other PLDs in the Altera MAX II family may include the number of macrocells, package size, and specific features. Please refer to the Altera datasheets for detailed comparisons.




