EP4CE55F23I7N FPGAs: Features, Applications and Datasheet
2025-04-10 10:27:40 1286
EP4CE55F23I7N Description
The EP4CE55F23I7N is a high-performance, cost-effective FPGA from Intel (formerly Altera), part of the Cyclone® IV E family. Designed for power-sensitive and space-constrained applications, this device delivers a balanced mix of logic elements, memory, and DSP blocks to support mid-range FPGA designs. Housed in a 484-ball FBGA package and rated for industrial temperature ranges, it's ideal for harsh environments while offering robust programmable logic capability.
EP4CE55F23I7N Features
Logic Elements (LEs): 55,000, offering substantial processing capacity.
Embedded Memory: Up to 2.48 Mb of on-chip RAM for faster data buffering and temporary storage.
DSP Blocks: Integrated multipliers enhance signal processing efficiency in audio, video, and control applications.
I/O Pins: 343 user I/Os to support complex board-level connectivity.
PLL Support: Phase-Locked Loops for precise clock management and timing control.
Low Power: Optimized for reduced power consumption without compromising performance.
Operating Temperature: -40°C to +100°C (industrial-grade reliability).
Package: FBGA-484, compact and suitable for dense PCB layouts.
EP4CE55F23I7N Applications
Industrial Automation: Real-time control systems, motor drives, and machine vision.
Communications: Baseband processing, protocol bridging, and network infrastructure.
Medical Equipment: Portable diagnostic devices and imaging systems.
Embedded Systems: Custom logic integration in IoT edge devices.
Video Processing: Frame buffering, video scaling, and real-time filtering.
Aerospace & Defense: Rugged systems requiring high reliability and flexible logic.
EP4CE55F23I7N CAD Model
Symbol
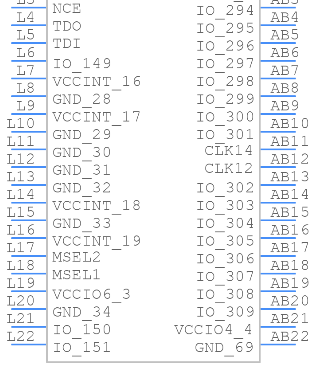
Footprint
3D Model

EP4CE55F23I7N Alternatives
Here are a few possible alternatives to the EP4CE55F23I7N based on performance and features:
EP4CE30F23I7N – Slightly lower logic elements (30K), ideal for less complex designs.
EP4CE115F29I7N – Higher capacity (115K LEs), suitable for more demanding applications.
LFE3-70EA-6FN484I (Lattice ECP3 family) – Comparable logic resources and power efficiency.
XC6SLX75-3FGG484I (Xilinx Spartan-6) – Alternative from Xilinx with similar capabilities.
EP4CE55F23I7N Manufacturer
Intel Corporation is a global technology leader renowned for pioneering advancements in semiconductor innovation. Founded in 1968 and headquartered in Santa Clara, California, Intel designs and manufactures a broad range of products, including microprocessors, chipsets, FPGAs, and AI accelerators. As the architect behind the x86 processor architecture, Intel has played a pivotal role in shaping modern computing—from personal computers and data centers to cloud infrastructure and edge devices. Today, Intel continues to drive innovation across high-performance computing, artificial intelligence, 5G, and embedded systems, empowering a smarter, more connected world.
EP4CE55F23I7N FAQs
1. What kind of configuration schemes are supported by EP4CE55F23I7N?
It supports multiple configuration methods including Active Serial (AS), Passive Serial (PS), JTAG, and Passive Parallel modes for design flexibility.
2. Can this FPGA support external memory interfaces like DDR2 or DDR3?
Yes, Cyclone IV FPGAs can support external memory interfaces, though support is more commonly robust for DDR and DDR2. Check the IP catalog and timing models for interface limitations.
3. How does the device manage clock domains and timing across different modules?
It includes global and regional clock networks along with PLLs for clock domain crossing and timing synchronization, essential for complex multi-clock systems.
4. Is there built-in ECC support for memory blocks in this FPGA?
While native ECC is not directly available in all memory blocks, designers can implement soft ECC logic to enhance data integrity in critical applications.
5. What design tools are used for developing with this FPGA?
Development is primarily done using Intel Quartus Prime (formerly Altera Quartus II), which provides synthesis, simulation, and programming tools tailored for Cyclone IV devices.




