EP4CE30F23C8N Intel FPGAs: Features, Applications and Datasheet
2025-06-11 11:00:15 727
EP4CE30F23C8N Description
The EP4CE30F23C8N is an entry-level member of Intel's (formerly Altera) Cyclone IV E FPGA family, engineered for low-power and cost-sensitive applications. Designed with 30K logic elements and housed in a compact 484-ball FBGA package, it balances affordability with sufficient logic density and embedded memory for mid-range digital logic designs.
EP4CE30F23C8N Features
Logic Elements (LEs): 28,416 for moderate to complex designs
Embedded Memory: 594 Kbits of RAM blocks for efficient data handling
High-Speed PLLs: 2 PLLs for flexible and accurate clock management
I/O Pins: Up to 332 general-purpose I/Os
Package: FBGA-484 with 0.8 mm pitch
Voltage Compatibility: Core voltage of 1.2V, with support for multiple I/O standards
Configuration Options: Supports JTAG and passive serial configuration modes
Low Power Operation: Optimized for low power usage in embedded systems
EP4CE30F23C8N Applications
Industrial Automation Controllers – Low-cost programmable logic for machinery and process control
Medical Imaging Systems – Signal processing support in devices like ultrasound or portable X-ray units
Consumer Electronics—Used in smart TVs, audio systems, and gaming gear
Wireless Communication Systems – Baseband signal processing and protocol bridging
Educational FPGA Development Boards – Ideal for lab experiments and university-level FPGA education
Data Acquisition Systems—Enables flexible timing and I/O interfacing in sensor-heavy systems
EP4CE30F23C8N CAD Model
Symbol
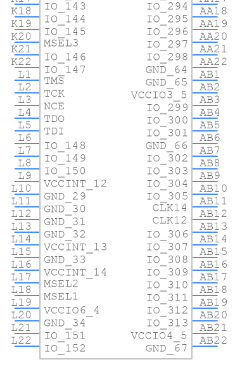
Footprint
3D Model

EP4CE30F23C8N Alternatives
If you're looking for similar performance but with variations in logic or resources, consider:
EP4CE22F17C8N – Lower logic element count, cost-effective option
EP4CE40F23C8N – Offers more LEs for larger designs in same package
LFE5U-25F-6BG381I (Lattice ECP5) – Comparable logic size, lower power alternative
XC6SLX25-2CSG324C (Xilinx Spartan-6) – Equivalent performance for Spartan-series designs
10CL025YU256C8G (Intel Cyclone 10 LP) – Newer generation with enhanced low-power benefits
EP4CE30F23C8N Manufacturer
Intel Corporation is a global leader in semiconductor innovation, specializing in the design and manufacturing of microprocessors, chipsets, FPGAs, and related technologies that power everything from personal computers to cloud data centers. Founded in 1968 and headquartered in Santa Clara, California, Intel pioneered the x86 architecture that underpins the majority of the world’s computing infrastructure. Over the decades, Intel has evolved beyond processors, investing in artificial intelligence, autonomous systems, networking, and memory technologies. With a focus on performance, scalability, and innovation, Intel continues to shape the future of computing and connectivity across diverse industries including consumer electronics, telecommunications, healthcare, and industrial automation.
EP4CE30F23C8N FAQs
What is the maximum clock frequency supported by EP4CE30F23C8N?
The maximum internal clock frequency typically ranges between 150–200 MHz, depending on design utilization and PLL configuration.
Does EP4CE30F23C8N support DDR memory interfaces?
No, the EP4CE30F23C8N does not natively support DDR2/DDR3 memory interfaces. For advanced memory protocols, Cyclone V or 10 series are recommended.
How many user I/O pins are available in the FBGA-484 package?
Up to 332 I/O pins are available, with support for multiple voltage standards and I/O banks.
What programming cable is needed for configuring this FPGA?
You can use Intel’s USB-Blaster or USB-Blaster II JTAG programming cables for configuration and debugging.
Is there a hard processor core inside the EP4CE30F23C8N?
No, this FPGA is a purely logic-based device and does not include an embedded processor core. For that capability, Cyclone V SoCs or Arria SoCs should be considered.




