EP3C5E144C8N FPGAs: Features, Applications and Datasheet
2025-07-07 10:35:13 503
EP3C5E144C8N Description
The EP3C5E144C8N is part of the Cyclone® III FPGA family from Intel (formerly Altera), designed for low power and high-volume applications. Packaged in a 144-pin EQFP form factor, this device offers 5,136 logic elements and is fabricated using a 65 nm low-power process. It strikes a balance between performance and cost-efficiency, making it ideal for a wide range of embedded and control-oriented designs.
EP3C5E144C8N Features
Logic Elements (LEs): 5,136 for implementing custom logic designs
Embedded Memory: 423 Kbits of RAM for data buffering and storage
PLL Support: 2 PLLs for high-precision clock generation and management
I/O Pins: 83 programmable I/O pins for versatile peripheral interfacing
Power Efficiency: Optimized for low static and dynamic power consumption
Package Type: 144-pin EQFP, suitable for compact PCB designs
Operating Temperature: Commercial grade (0°C to +85°C)
EP3C5E144C8N Applications
Consumer Electronics: Used in devices like digital cameras, gaming consoles, and home appliances
Industrial Control: Ideal for PLCs, automation controllers, and smart sensors
Communications: Suitable for network protocol bridging, low-speed serial communication
Medical Devices: Employed in cost-sensitive portable diagnostic equipment
Educational Tools: Common in university-level FPGA development kits and projects
EP3C5E144C8N CAD Model
Symbol
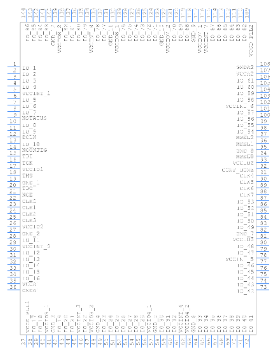
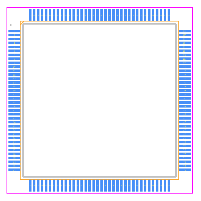
Footprint
3D Model
EP3C5E144C8N Alternatives
Here are a few alternatives with similar logic capacity or footprint:
EP3C5F256C8N: Same logic capacity with a different 256-pin FBGA package
EP4CE6E22C8N: Higher-performance Cyclone IV device with 6,272 logic elements
LFE5U-12F-6MG285C (Lattice ECP5): A comparable low-power FPGA from Lattice
XC6SLX9-2TQG144C (Xilinx Spartan-6): Close logic density and pin-count from Xilinx
EP3C5E144C8N Manufacturer
Intel Corporation is a global technology leader known for designing and manufacturing innovative semiconductor products, including microprocessors, chipsets, and integrated circuits. Founded in 1968 and headquartered in Santa Clara, California, Intel pioneered the x86 architecture and remains one of the world’s largest and most influential chipmakers. Its processors power a vast range of computing devices—from personal computers and servers to embedded systems and IoT platforms. In addition to CPUs, Intel also offers solutions in AI, networking, graphics, and memory technologies. With a strong focus on research, sustainability, and manufacturing excellence, Intel continues to shape the future of computing worldwide.
EP3C5E144C8N FAQs
1. Does EP3C5E144C8N support in-system programming (ISP)?
Yes, it supports ISP via the JTAG interface, allowing users to update the configuration memory without removing the chip from the board.
2. What is the typical power consumption profile for this device?
Under normal operating conditions, the EP3C5E144C8N consumes around 85–150 mW, making it suitable for battery-powered systems and thermally constrained environments.
3. Can this FPGA interface directly with 3.3V logic levels?
Yes, the I/O banks support various voltage standards including 3.3V LVCMOS, making it compatible with common microcontroller and peripheral logic levels.
4. Is the EP3C5E144C8N suitable for high-speed serial communication?
This specific model lacks integrated SERDES blocks, so while it supports basic serial protocols like UART, SPI, and I²C, it is not ideal for high-speed transceiver applications.
5. What is the configuration file format used for programming this FPGA?
The device uses a .sof (SRAM Object File) for configuration during development and a .pof (Programming Object File) for programming non-volatile configuration devices like EPCS serial flash.




