EN5322QI DC-DC Converters: Features, Applications and Datasheet
2025-10-17 14:37:03 531
EN5322QI Description
The EN5322QI is a highly integrated power system-on-chip (PowerSoC) designed by Intel (formerly Enpirion). It delivers a complete DC-DC step-down solution, integrating the inductor, MOSFETs, and compensation network into a compact package. The device provides a regulated output voltage from a 2.4V to 5.5V input voltage range, capable of delivering up to 2A continuous output current with high efficiency and minimal external components. Its compact QFN package and minimal footprint make it ideal for space-constrained power management designs.
EN5322QI Features
Integrated inductor and MOSFETs for a compact, low-profile solution.
2.4V to 5.5V input voltage range with programmable output voltage.
Up to 2A continuous output current.
High efficiency over a wide load range.
Internal compensation for simplified design.
Fast transient response and stable operation with low-ESR capacitors.
Over-current and over-temperature protection.
Small 5mm × 5mm QFN package for minimal PCB area.
EN5322QI Applications
FPGA, DSP, and ASIC power supplies.
Networking and telecommunication equipment.
Industrial control and automation systems.
Portable and handheld electronics.
Consumer and computing devices requiring high power density.
EN5322QI CAD Model
Symbol
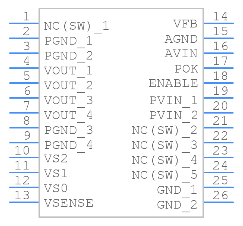
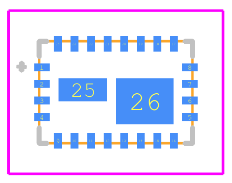
Footprint
3D Model
EN5322QI Alternatives
EN5311QI – 1A PowerSoC with similar footprint but lower output current.
EN5339QI – 3A PowerSoC for higher load applications.
TPS82130 from Texas Instruments – 3A MicroSiP DC-DC converter.
Murata OKI-78SR series – compact non-isolated switching regulators.
Analog Devices ADP2302 – 2A step-down regulator with external inductor.
EN5322QI Manufacturer
Intel Corporation is a global technology leader headquartered in Santa Clara, California, USA. Founded in 1968 by Robert Noyce and Gordon Moore, Intel is best known for pioneering the development of microprocessors—the central processing units (CPUs) that power most of the world’s computers. Over the decades, Intel has expanded its expertise beyond CPUs to include advanced semiconductor manufacturing, artificial intelligence, networking, graphics, and cloud-to-edge computing technologies.
As one of the largest semiconductor companies in the world, Intel designs and manufactures a wide range of products including processors, chipsets, FPGA (Field Programmable Gate Arrays), SoCs (System-on-Chip), memory, and power management solutions. The company continues to drive innovation through cutting-edge process technologies, such as Intel 4 and Intel 3 nodes, and through its IDM 2.0 strategy—combining internal manufacturing, external foundry use, and the expansion of Intel Foundry Services (IFS).
Intel’s technologies play a vital role in enabling digital transformation across industries—from personal computing and data centers to automotive and industrial applications. With a strong focus on sustainability, security, and performance, Intel continues to shape the future of computing and connectivity for a smarter, more efficient, and data-driven world.
EN5322QI FAQs
What is the typical switching frequency of the EN5322QI?
The EN5322QI operates at a fixed switching frequency of approximately 4 MHz, allowing the use of small passive components and reducing output ripple.
Can the EN5322QI be synchronized with an external clock?
No, the EN5322QI operates with an internal fixed-frequency oscillator and does not support external synchronization.
What is the recommended output capacitor type for stable operation?
The EN5322QI is optimized for ceramic capacitors (X5R or X7R dielectric) with low ESR for best transient and ripple performance.
Does the EN5322QI support output voltage sequencing or tracking?
The device supports controlled startup and soft-start, but for precise voltage tracking, external control circuitry is required.
How does the EN5322QI protect against overcurrent conditions?
The converter includes cycle-by-cycle overcurrent protection that limits the peak inductor current, ensuring device and system safety under fault conditions.




